Light calcium carbonate modification improves its properties for specific industrial uses. This modification can use various techniques. They include surface treatment and adding functional additives. These improve properties like dispersibility, stability, and compatibility with other materials.
Limestone is used to make light calcium carbonate. It’s heated to make lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide. Then, water is added to make lime milk (calcium hydroxide). Carbon dioxide is then added to make calcium carbonate. It’s then dried and crushed.
Light calcium carbonate production technology and equipment
In the industry, light calcium carbonate is generally produced through carbonization. The carbonization reaction system is in the carbonization method. It is a gas-liquid-solid three-phase system. It mainly includes the following stages:
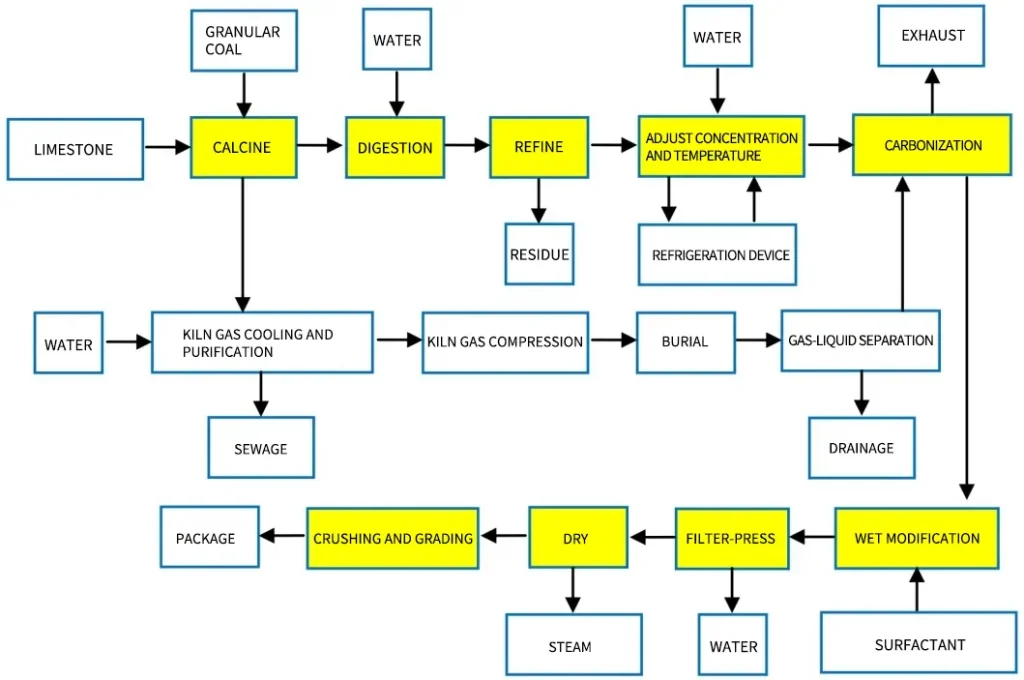
Lime and coal are mixed in a certain proportion. Then, they are heated in a mixing shaft kiln to make calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
Digestion: Calcined lime is deslagged. It is then enters the digestion tank to react with water to make lime milk.
Carbonization happens after the lime milk is refined. It reacts with kiln gas at a certain temperature and concentration. Then, it undergoes carbonization.
Dehydration, drying, and grading: filter press dehydration, drying, crushing, grading, and packaging.
Calcination
Limestone calcination is key in making good light calcium carbonate. It also saves energy and reduces consumption. It is not just about the energy use of making quicklime. It also affects the overall process’s energy use. Most domestic enterprises use mixed-material vertical kilns. They use them to calcine limestone. More advanced enterprises use steel shell vertical kilns. They have high mechanization and a complete structure. Quite a few enterprises still use vertical kilns with brick-concrete structures. A few enterprises use advanced gas-fired vertical kilns. They also use single-tube and double-tube kilns. These kilns have parallel flow thermal storage. They are from abroad.
New vertical kiln:
calcining limestone with gas fuel or liquid fuel instead of coal and coke. Change the mixed-material type to a direct-fired type. Also, use parallel flow and thermal storage types. Also, use magnetic cylinder types and other vertical kilns for calcination. The lime industry has shown that using gas and liquid fuel in vertical kilns has many benefits. It has shown this both at home and abroad. These include the economy, technology, product quality, worker safety, and how hard the work is.
Rotary kiln:
The limestone is calcined in a rotary kiln with gas or liquid as fuel. The limestone particles are 5-10mm. The calcination temperature is reduced to 800-1100℃. The lime produced has many advantages. It has high activity, no pollution, and is easy to digest. Also, it requires only a small amount of slag removal. It has been successfully used in the production of light calcium carbonate abroad.
Suspension calcining furnace:
This equipment has these traits. Combustion, heat transfer, and decomposition happen in the same space. Also, flameless combustion and flash heat transfer happen instantly. The gas-solid phase reaches a stable temperature instantly. The system is closed and operates at negative pressure. It is safe and hygienic. It can be controlled with a microcomputer. It has high automatic control. It makes stable, unpolluted products. This equipment has mature technology and equipment in the production of cement industry.
Cyclone dynamic calcining furnace:
This equipment mixes the calcined material with the hot gas. It completes the instant calculation in the flow. It has an adjustable temperature and operates continuously. It keeps an even gas-solid temperature in the furnace and transfers heat fast. It has a small temperature difference in the material. It uses little energy and operates a closed system. It pollutes neither the material nor the environment. It also has easy, automatic adjustment. It is being promoted in China and has successful experience in calcining kaolin.
This is an active lime calcining furnace. It uses bituminous coal as fuel. It heats limestone indirectly. The limestone meets the special quality requirements in ZDB6001-85. The lime’s activity reaches 330-360 degrees (mL). The furnace makes active lime by heating limestone. The lime is not polluted by sulfur and other harmful elements, dust, etc. in the flue gas from burning coal. It is also very active and does not add carbon. The CO2 gas is made during calcination. It does not mix with the flue gas. It is pure and can be recycled.
Carbonization
The carbonation reaction is a key step. It’s in the making of calcium carbonate. The towers have different structures. The structures cause different volumes, flow rates, contact areas, and contact speeds. These factors affect the reactants: carbon dioxide gas and calcium hydroxide emulsion. These variables directly affect the quality and quality of calcium carbonate crystals.
Now, the most used carbonization towers include bubbling and spray types. There are also intermittent stirring towers and ultra-gravity devices. The shape and size of particles will change in the carbonization process. This change will be due to the shape controller and conditions. These conditions include temperature, calcium hydroxide concentration, stirring speed, and CO2 ventilation.
Dry
In making light calcium carbonate, drying is a main energy user. It also affects product quality. It does this by controlling impurities like black spots, pH, and sediment. So, it is urgent to pick drying equipment with low energy use, high capacity, and green tech.
Light calcium carbonate companies often use drum dryers. They also use rotary tube dryers, mesh belt dryers, disc dryers, paddle dryers, and rotary flash dryers for drying.
Of course, some companies also use a two-level combo. They use it to dry light calcium carbonate. For example, a company in Sichuan uses rotary flash drying. They also use the hollow paddle drying process. First, it uses rotary flash drying’s fast drying and crushing effect. It dries the calcium carbonate filter cake from 35% to about 8%. Then, it goes into the hollow paddle dryer to reach less than 0.2% moisture.
Light calcium carbonate surface modification technology and equipment
The way calcium carbonate disperses and modifies it directly affects its use. It also affects where it can be applied. It is a key technology for the calcium carbonate industry. The tech for spreading and changing light calcium carbonate is even more important. It’s more important than the process for making calcium carbonate. The surface of light calcium carbonate is modified in two ways: wet and dry.
Wet activation is to add an activator to a solvent, such as water. Then, stir the calcium carbonate in it to coat its surface. Finally, dry it. This is usually done in companies. They make light or nano calcium carbonate. Common surface modifiers include stearic acid (salt), phosphate, and condensed phosphoric acid. They also include quaternary ammonium salt surfactants. The wet method is a traditional calcium carbonate surface treatment method. It works with water-soluble surfactants. The advantages of this method are uniform coating and high production quality. However, drying requires the control of certain temperatures and conditions. Some surface treatment agents are insoluble in water or easily decomposed in water. The use of other organic reagents has cost and safety issues.
One dry modification method is to put calcium carbonate powder into the modifier. Then, add the surface modifier. Use the mixer and heat to make it stick to the calcium carbonate. This makes the particles modified.
The equipment for dry surface modification is the same for light and heavy calcium carbonate. It mainly includes CRM three-roller continuous powder surface modifier. It also has pin mill, cell mill, and eddy turbo mill modifiers.
Several dry modification equipment
Recently, light calcium carbonate modification has gained attention in plastics, rubber, and paints. By tailoring light calcium carbonate, manufacturers can improve their products. This leads to better durability, lower costs, and higher quality.