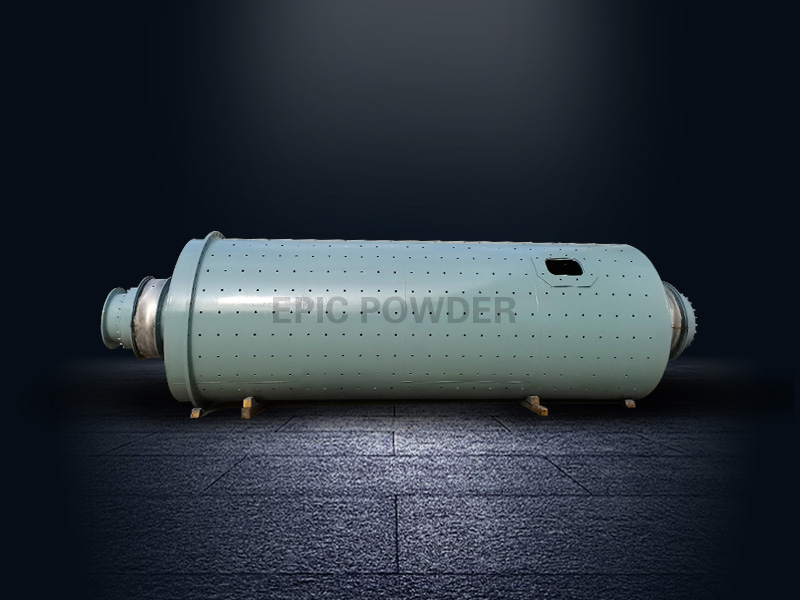
Ball mill is a grinding device that turns material into fine powder. Ball mills are cylindrical. They are the main grinder for mashing paints, ores, ceramics, and some hard chemicals. A ball mill can effectively convert a hard material into a loose powder by rotating on a horizontal axis. This equipment is popular in industries like mining, ceramics, and powder processing. It breaks down non-metallic minerals, including calcium carbonate, quartz, and alumina. A ball mill has a rotating cylindrical shell. It’s filled with grinding media, like steel or ceramic balls. These balls grind the material through impact and friction. They boost productivity by turning hard materials into finer particles. This happens through rotating drums and milling media.

Definition and Working Principle of ball mill
As mentioned earlier, a ball mill is a grinder used to grind or blend materials for mineral dressing processes, paints, pyrotechnics, ceramics, and selective laser sintering. It works on the principle of impact and attrition: size reduction is done by impact as the balls drop from near the top of the shell. A ball mill consists of a hollow cylindrical shell rotating about its axis. The axis of the shell may be either horizontal or at a small angle to the horizontal. It is partially filled with balls. The grinding media are the balls, which may be made of steel, stainless steel, ceramic, or rubber. The inner surface of the cylindrical shell is usually lined with an abrasion-resistant material such as manganese steel or rubber. The balls occupy about 30 to 50 percent of the volume of the ball milling.
Key Components of a Ball Mill
Cylindrical Shell: Rotates on a horizontal axis and contains the material and grinding media.
Grinding Media: Balls made of steel, ceramic, or other materials that crush particles into a fine powder.
Drive System: Powers the rotation of the shell.
Feed and Discharge Ports: For material to enter and exit after grinding.
Types of Ball Mills
Planetary Ball Mill: Suitable for fine and ultra-fine grinding with high energy efficiency.
Horizontal Ball Mill: Common in industrial applications for coarse and fine grinding.
Vibration Ball Mill: Uses vibration to enhance grinding efficiency.
Particle Size Range
Ball mills can grind materials to particle sizes ranging from about 10 microns to a few millimeters, depending on the mill type, grinding time, and grinding media size. This flexibility makes ball mills ideal for various applications, from coarse grinding to fine powder production.
Advantages of ball mill
- Suitable for both wet and dry grinding processes: The ball milling can perform dry grinding or wet grinding depending on the properties of the material being processed.
- High production capacity and continuous operation: With the ability to grind multiple materials, the ball millingcan output a continuous stream of powdered material.
- Low energy consumption: The ball milling consumes less energy during operation due to the rotating motion of the grinding media.
- Versatility in grinding materials: The ball milling can grind various materials, including cement, pyrotechnics, ceramics, and selective laser sintering.
- Easy maintenance and operation: The ball milling requires minimal maintenance and is easy to operate, making it suitable for experienced and inexperienced operators.
Disadvantages of ball milling
- High equipment cost: The initial investment for a ball milling is relatively high, especially for larger mills with higher capacity. This can make it challenging for small-scale production or those with limited financial resources.
- Not suitable for ultra-fine grinding: The final particle size achievable with a ball mill is limited, making it unsuitable for ultra-fine grinding applications.
- Noise and vibration: During operation, the ball milling can generate noise and vibration, which can be a nuisance in certain environments.
- Risk of over-grinding: Over-grinding can produce fines that are too small for the desired application, wasting energy and reducing the overall efficiency of the grinding process.
Why Ball Mills Still Matter
- Simple design and solid performance for a wide range of industrial powder processing
- Effective for grinding non-metallic minerals like quartz, alumina, and calcium carbonate
- Easy to maintain with established workflows across the U.S. market
Modern Alternatives and Their Strengths
- Jet Mills: Ideal for micronization and producing ultra-fine powders with minimal contamination and heat build-up
- Air Classifier Mills: Offer precise particle size distribution control and lower energy consumption
- Both types reduce grinding media wear and maintenance costs
The EPIC Powder Machinery Edge
- Combines the reliability of traditional ball milling with modern tech innovations
- Customizable systems for enhanced efficiency, reduced energy use, and better powder quality
- Strong support and service network across the U.S. helps companies seamlessly switch or upgrade
In , if your grinding tasks require standard size reduction, a ball mill remains a go-to device. But when fine powder grinding or energy savings are critical, EPIC Powder Machinery’s modern solutions step in to provide an edge over traditional ball mills.
If your needs are not met by a ball mill, you need to learn about other grinding equipment. For a more in-depth comparison of when to choose a jet mill or air classifier mill instead of a ball mill, check out EPIC’s detailed guide on jet mill or air classifier mill making the best choice.
Applications of ball mill
- Cement industry: The ball mill is commonly used for grinding cement clinker and gypsum to produce cement.
- Mineral processing: The ball milling is widely used in ore processing plants to grind various ores and other materials.
- Ceramic industry: The ball milling grinds different ceramic materials, such as clay, quartz, and feldspar.
- Pharmaceutical industry: The ball milling grinds and mixes pharmaceutical products for drug formulation.
- Paint and coating industry: The ball mill grinds and disperses pigments in paint and coating production.
Ball mill and classifier production line case from EPIC Powder Machinery
If you would like to learn more about our ball mill and classifier production line and get a free quote, please contact us.
Ball milling and classifying production line on-site video
When to Choose a Ball Mill Niche Use Cases
Ball mills are a solid choice in many industrial powder processing tasks. Here’s when you should consider using one:
Ideal Use Cases for Ball Mills
| Use Case | Why Ball Mill Works Best |
|---|---|
| Grinding Non-metallic Minerals | Handles hard materials like quartz and alumina efficiently |
| Producing Fine Powder | Great for achieving uniform particle size distribution in powders like calcium carbonate |
| Batch and Continuous Milling | Flexible for both small batches and large-scale production |
| Ceramic and Chemical Processing | Resistant liners and grinding media suit abrasive materials |
| Mineral Grinding | Can grind a variety of ores due to versatile grinding media types |
| Laboratory Scale Testing | Easy to control variables for small sample preparation |
Key Points to Consider
- Material Hardness: Best for brittle and hard materials.
- Particle Size Control: Helps get a consistent particle size.
- Energy Efficiency: Suitable when energy consumption is manageable.
- Maintenance: Prefer when maintenance costs and downtime are acceptable.
If your job involves fine grinding with a need for consistent results on tough materials, a ball mill usually meets those needs well. For industries around the world dealing with industrial powder processing, the ball mill remains a dependable choice in many niche applications.
When to Upgrade to EPIC Powder Machinery
If your current ball mill isn’t cutting it anymore, it might be time to consider upgrading to EPIC Powder Machinery. Here’s how to know when an upgrade makes sense:
- High energy consumption: Older ball mills often use more power than necessary. EPIC machines are designed for better efficiency, helping you save on energy costs.
- Maintenance headaches: If you’re spending too much time and money on ball mill maintenance, EPIC’s durable parts and advanced designs can cut downtime and maintenance costs.
- Need finer powders: When your product demands ultra-fine particle size distribution for industrial powder processing, EPIC’s precision grinding technology delivers better results.
- Production bottlenecks: If your ball mill limits your production capacity, EPIC Powder Machinery offers faster throughput and improved grinding performance.
- Looking for modernization: Comparing air classifier mill vs ball mill or jet mill options? EPIC offers state-of-the-art solutions that combine the best of traditional and modern milling.
- Your application demands it: For specialized materials like calcium carbonate, quartz, or alumina, EPIC Powder Machinery provides tailored systems that enhance grinding efficiency and product quality.
Upgrading to EPIC Powder Machinery means stepping into efficient, reliable powder processing that meets the unique demands of U.S. industries — all while keeping energy and maintenance costs in check.
FAQs
What is the basic working principle of a ball mill?
A ball mill works by rotating a cylinder filled with grinding media like steel or ceramic balls. As the cylinder rotates, the balls collide with the material inside, breaking it down into finer particles.
What types of grinding media are used in ball mills?
Common grinding media include steel balls, ceramic balls, and sometimes flint or other materials, chosen based on the material to be ground and desired particle size.
How fine can ball mills grind materials?
Ball mills can grind materials down to a very fine powder, typically in the range of microns to submicron sizes, depending on the mill type and grinding conditions.
Are ball mills energy efficient?
Ball mills tend to consume more energy compared to some modern alternatives like jet mills or air classifier mills, but they offer reliable performance for a broad range of applications.
What maintenance is required for ball mills?
Regular maintenance includes inspecting and replacing worn liners, checking the grinding media, and ensuring the mechanical parts are well-lubricated to minimize downtime and reduce maintenance costs.
How do ball mills compare to other fine powder grinding equipment?
While ball mills are versatile and effective, options like jet mills offer better control over particle size distribution with lower heat generation but at higher capital costs.
When should I consider upgrading from a ball mill to modern machinery?
If you need finer particles with consistent quality, lower energy consumption, or reduced maintenance, it’s time to explore advanced solutions like the ones at EPIC Powder Machinery.
For more detailed insights, check out The Industrial Magic of Ultrafine Powder and learn how to optimize your grinding process.



