There are many methods for powder surface modification, and their classification varies depending on the perspective of the analysis. Based on the nature of the modification process, powder surface modification methods can be divided into six categories: surface coating modification, surface chemical modification, mechanochemical modification, capsule modification, high-energy modification, and precipitation reaction modification. Additionally, powder surface modifiers play a crucial role in these methods, effectively enhancing the surface properties and compatibility of powders, and are widely used in various fields.

Classification of Powder Surface Modification Methods
Surface Coating Modification
Surface coating modification involves the interaction of surface modifiers with particle surfaces without chemical reactions. The coating material adheres to the particles through van der Waals forces. This method is applicable to surface modification of various inorganic particles. It mainly utilizes inorganic or organic compounds to coat the particles, reducing their agglomeration. Due to the coating, steric hindrance is generated, making it difficult for the particles to re-agglomerate. Surface modifiers used in coating include surfactants, dispersing agents, and inorganic substances.
Surface Chemical Modification
Surface chemical modification is achieved by the chemical reaction or adsorption of surface modifiers with the particle surface.
Mechanical Chemical Modification
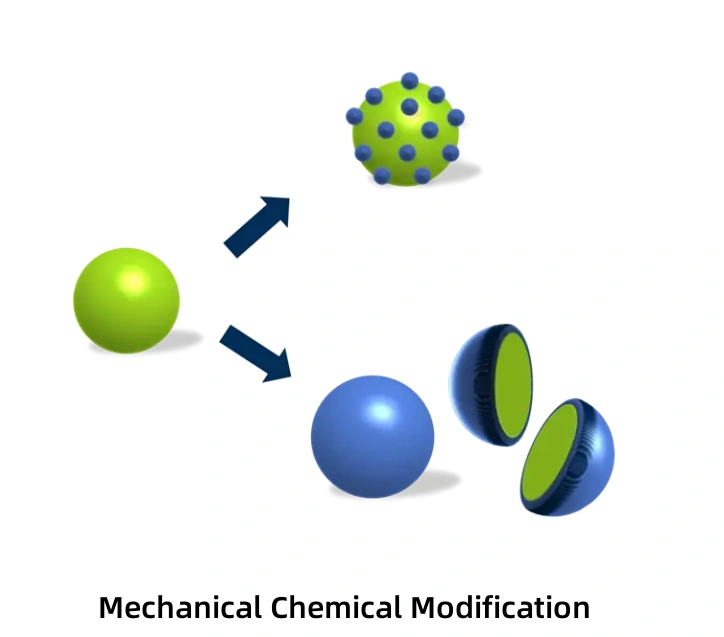
Mechanical chemical modification refers to the use of mechanical methods such as crushing, grinding, and friction. These methods change the mineral lattice structure and crystal form, increase the system’s energy, raise the temperature, and promote the dissolution, thermal decomposition, or generation of free radicals or ions. This enhances the mineral surface activity and promotes reactions or adhesion with other substances to achieve surface modification.
Precipitation Reaction
Precipitation reaction involves adding a precipitant to a solution containing powder particles or adding substances that trigger the formation of precipitant in the reaction system. The modification ions undergo a precipitation reaction, precipitating on the particle surface to form a coating. The precipitation method can be divided into direct precipitation, homogeneous precipitation, heterogeneous precipitation, co-precipitation, hydrolysis, and others.
Capsule Modification
Capsule modification is a surface modification method where a uniform and certain thickness film is covered on the powder particles.
High-energy Modification

High-energy modification is a method that induces polymerization reactions through plasma or radiation treatment.
There are many types of surface modifiers, and a unified classification standard has not yet been established. According to the chemical properties of the surface modifiers, they can be divided into organic and inorganic modifiers. These are used for organic and inorganic surface modification of powders. Surface modifiers include coupling agents, surfactants, low molecular weight polyolefins, and inorganic modifiers.
Powder surface modification generally has specific application backgrounds or fields. Under the premise of meeting technical requirements or user needs, the economic, safety, and environmental factors are comprehensively considered. It is essential to choose surface modifiers that are cost-effective, safe, and environmentally friendly, as much as possible.
Common Powder Surface Modifiers and Their Applications
Powder Surface Modifiers 1
Surface Modifier Name: Titanium Ester Coupling Agent
Varieties: Monohydroxy Type (NDZ-101, JN-9, YB-203, JN-114, YB-201, T1-1, T1-2, T1-3, etc.); Chelating Type (YB-301, YB-401, JN-201, YB-403, JN-54, YB-404, JN-AT, YB-405, T2-1, T3-1, etc.); Coordination Type (KR-41B, KR-46, etc.)
Applications: Calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, magnesium oxide, titanium oxide, zinc oxide, iron oxide, talc, wollastonite, barite, aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, montmorillonite, etc.
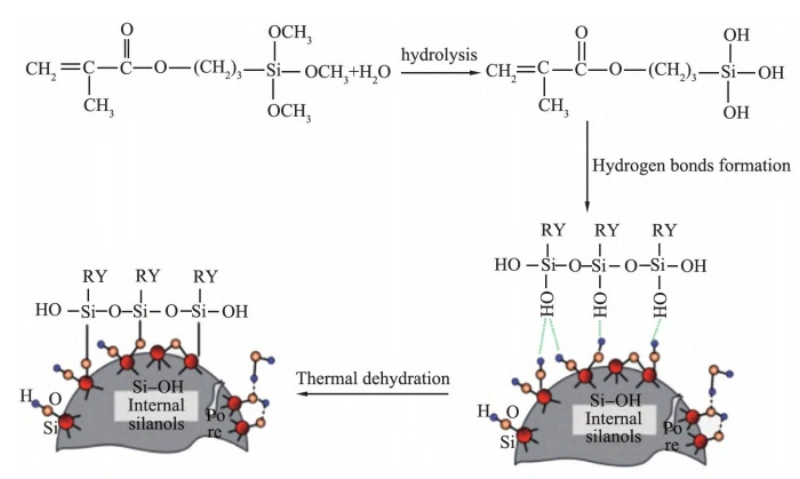
Powder Surface Modifiers 2
Surface Modifier Name: Silane Coupling Agent
Varieties: Amino Silane (SCA-1113, SCA-1103, SCA-603, SCA-1503, SCA-602, SCA-613, etc.); Epoxy Silane (KH-560, SCA-403, etc.); Sulfur Silane (KH-590, SCA-903, D-69, etc.); Vinyl Silane (SCA-1603, SCA-1613, SCA-1623, etc.); Methylpropyl Acyl Silane (SCA-503); Silane Ester (SCA-113, SCA-103, etc.)
Applications: Quartz, silica, glass fibers, kaolin, talc, wollastonite, aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, mica, montmorillonite, sepiolite, tourmaline, etc
Powder Surface Modifiers 3
Surface Modifier Name: Aluminum Ester Coupling Agent
Varieties: DL Series: 411-A, 411-B, 411-C, 411-D, 412-A, 412-B, 414, 481, 881, 882, 452, 471, 472, etc.; F Series: F-1, F-2, F-3, F-4, etc.; H Series: H-2, H-3, H-4; L Series: L-1A, L-1B, L-IH, L-2, L-3A
Applications: Calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, kaolin, talc, wollastonite, iron oxide, barite, aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide, fly ash, gypsum powder, mica, montmorillonite, etc.
Powder Surface Modifiers 4
Surface Modifier Name: Aluminum-Titanium Composite Coupling Agent
Varieties: FT-1, FT-2
Applications: Talc, wollastonite, iron oxide, kaolin, sepiolite, mica, montmorillonite, etc.
Powder Surface Modifiers 5

Surface Modifier Name: Anionic Surfactant
Varieties: Stearic acid (salts), sulfonates and their esters, high-grade phosphate ester salts
Applications: Light calcium carbonate, heavy calcium carbonate, wollastonite, bentonite, kaolin, magnesium hydroxide, talc, montmorillonite, etc.
Surface Modifiers 6
Surface Modifier Name: Cationic Surfactant
Varieties: High-grade amine salts (primary, secondary, tertiary amines, and quaternary ammonium salts)
Applications: Light calcium carbonate, heavy calcium carbonate, wollastonite, bentonite, kaolin, magnesium hydroxide, talc, montmorillonite, etc.
Surface Modifiers 7
Surface Modifier Name: Nonionic Surfactant
Varieties: Polyethylene glycol-based, polyol-based
Applications: Light calcium carbonate, heavy calcium carbonate, wollastonite, bentonite, kaolin, magnesium hydroxide, talc, montmorillonite, etc.
Surface Modifiers 8

Surface Modifier Name: Water-Soluble Polymer
Varieties: Polyacrylic acid (salts), polyacrylic acid (salts) and their copolymers, polyvinyl alcohol, polymaleic acid, etc.
Applications: Calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate, wollastonite, talc, red iron oxide, pigments, etc.
Surface Modifiers 9
Surface Modifier Name: Organosilicon
Varieties: Dimethylsilicone, methylsilicone, hydroxy silicone, hydrogen-containing silicone, etc.
Applications: Silica, kaolin, pigments, etc.
Surface Modifiers 10
Surface Modifier Name: Organic Oligomer
Varieties: Amorphous polypropylene, polyethylene wax, epoxy resin, etc.
Applications: Silica, mica, calcium carbonate, etc.
Surface Modifiers 11
Surface Modifier Name: Unsaturated Organic Acids
Varieties: Acrylic acid, methacrylic acid, oleic acid, maleic acid, cinnamic acid, octanoic acid, sorbic acid, chloropropionic acid, etc.
Applications: Feldspar, ceramic clay, red clay, aluminum hydroxide, silica, etc.
Surface Modifiers 12
Surface Modifier Name: Inorganic Surface Modifiers
Varieties: Titanium salts, chromium salts, iron salts, silicates, aluminum salts, magnesium salts, zirconium salts, zinc salts, cadmium salts, etc.
Applications: Mica, kaolin, talc, titanium dioxide, alumina, magnesium oxide, pigments, etc.
Epic Powder
In conclusion, Epic Powder provides a comprehensive range of powder surface modification solutions, utilizing advanced equipment tailored for various applications. With our extensive expertise in grinding and modification technologies, we offer custom solutions that meet the specific needs of different industries. By incorporating a variety of powder surface modifiers, including titanium esters, silane coupling agents, and organic silicones, our equipment ensures high-quality, efficient, and environmentally friendly surface modification. Whether you are working with calcium carbonate, silica, or other inorganic materials, Epic Powder’s state-of-the-art technology guarantees optimal performance and value.
