The particle size range of spherical silver powder used in crystalline silicon solar front-side silver paste is 1.0–3.0 μm, while conventionally synthesized silver powder usually has a wide particle size distribution. Therefore, the prepared silver powder must undergo classification treatment to meet the requirements for silver powder used in crystalline silicon solar cell electrode silver paste.
Performance Requirements of Silver Powder in Photovoltaic Silver Paste
The requirements for silver powder in photovoltaic silver paste are not only reflected in particle size distribution but also include:
- Narrow particle size distribution: Ensures stable slurry fluidity and clear screen-printed lines.
- High sphericity: Reduces specific surface area, lowers slurry viscosity, and decreases organic carrier consumption.
- Good dispersibility: Prevents agglomeration and ensures uniform slurry film formation.
- Low impurity content: Guarantees electrode conductivity and long-term reliability.
- Precisely controlled particle size: Especially for the 1–3 μm mid-range silver powder, which is critical for electrode density and conductivity.
Thus, classification is a key step in the preparation of silver powder.
Current Classification Methods for Ultrafine Silver Powder
At present, the industry mainly adopts mechanical vibration sieving and air classification for ultrafine silver powder.
Mechanical Vibration Sieving
Mechanical vibration sieving is a traditional method that uses mechanical or ultrasonic vibration to pass silver powder through sieves of different mesh sizes.
Features:
- Advantages: Simple operation, low cost, suitable for preliminary classification.
- Disadvantages:
- When mesh size exceeds 800 mesh (about 18 μm and below), metallic powders tend to block sieve openings, reducing efficiency.
- Ineffective for micro-sized or submicron silver powder.
- Powder agglomeration during sieving reduces precision.
Application Example:
A patented device combines inclined sieves with a vibration motor, ensuring even powder distribution on the sieve surface for quick classification. By changing sieve meshes, users can obtain silver powder of different sizes. This method is mainly useful for initial screening in silver powder production.
Air Classification

Air classification is currently the most widely used method for ultrafine silver powder. Its principle is to use air as the classification medium and rely on the high-speed rotation of a classifier wheel combined with centrifugal forces to separate particles of different sizes.
Features:
- Controllable classification size range (down to submicron level).
- Well-dispersed particles with minimal agglomeration.
- Narrow particle size distribution, ideal for photovoltaic silver paste.
- Adjustable parameters (classifier wheel speed, blower frequency, feed rate) for precise particle size control.
Application Example:
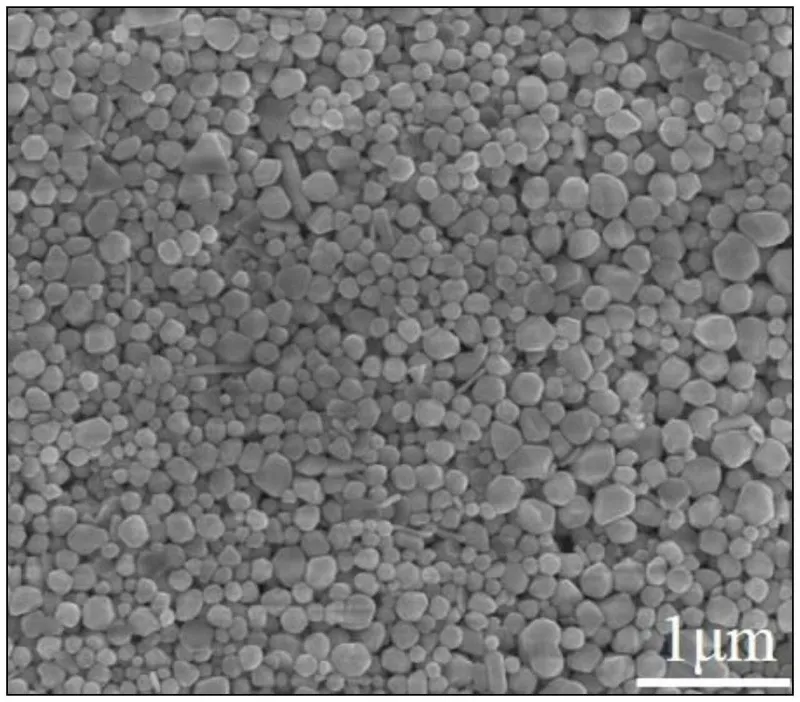
Researchers have used a single-stage air classifier to process silver powder and found that, under optimized classifier wheel speed, 1–3 μm spherical silver powder can be precisely classified. The resulting product had a narrower size distribution, and when made into front-side silver paste, it significantly improved the photoelectric conversion efficiency of solar cells.
For powders below 1 μm, a two-stage classification system can be adopted: the first stage for coarse classification (D50 ≈ 3 μm), the second for fine classification (D50 ≈ 1 μm). Coupled with a cyclone collector, the fine powder recovery rate can reach 92%.
Equipment Selection and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Common Air Classifier Types
- Turbine Air Classifier
- Forms a strong centrifugal field through high-speed rotating classifier wheel.
- Suitable for micron-sized silver powder.
- High efficiency, precise particle size control.
- Multi-Rotor Air Classifier
- Multiple classifier wheels operating in parallel to increase throughput.
- Produces narrower particle size distribution.
- Commonly used in large-scale silver powder production lines.
- Inert Gas-Protected Air Classifier
- Uses nitrogen or argon as the classification medium.
- Prevents oxidation of silver powder during classification.
- Suitable for high-purity silver powder production.
Technology Comparison
| Technology | Advantages | Limitations | Suitable Application |
| Mechanical Vibration Sieving | Low cost, simple operation | Low precision, sieve blockage issues | Initial screening, coarse particle removal |
| Air Classification | Narrow distribution, high precision, controllable | Higher cost, greater energy consumption | Precision classification for photovoltaic silver powder |
Conclusion
With the rapid advancement of the photovoltaic industry and the rising demand for high-performance silver paste, silver powder classification technology is becoming increasingly critical. Air classification, with its precision and controllability, has gradually become the mainstream solution for achieving narrow particle size distributions in the 1–3 μm range.
Epic Powder, with its expertise in ultrafine powder processing and advanced air classification technology, provides reliable and customized solutions for silver powder production, helping manufacturers improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure stable performance in photovoltaic applications.
