The coating modification of titanium dioxide (TiO₂) is an important method to improve its properties, such as dispersion, weather resistance, gloss, and chemical stability. Through titanium dioxide coating modification, the performance of TiO₂ can be significantly enhanced for various industrial applications. Common coating methods are mainly divided into three categories: inorganic coating, organic coating, and composite coating. Below is a specific classification and brief introduction of these titanium dioxide coating modification methods, highlighting their unique benefits for various applications.

Inorganic coating modification
By coating a layer of inorganic oxides or salts on the surface of titanium dioxide particles, a physical barrier is formed to improve its chemical stability and optical properties.
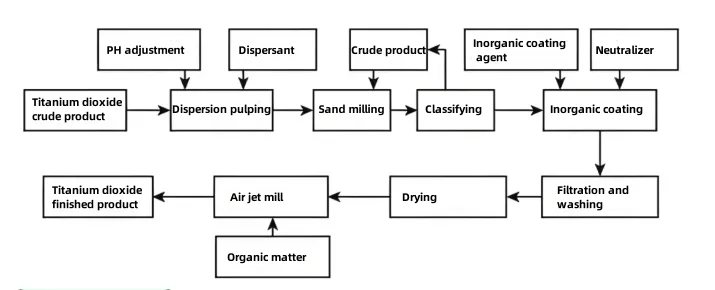
Oxide coating
Principle: Metal oxide hydrates (e.g., SiO₂, Al₂O₃, ZrO₂) precipitate on the TiO₂ surface to form a uniform coating layer.
Common Types:
- Silica (SiO₂) coating: Improves dispersion and weather resistance, reduces agglomeration, used in coatings and plastics.
- Alumina (Al₂O₃) coating: Enhances surface polarity, improves compatibility with organic matrices, increases gloss and chemical resistance.
- Zirconia (ZrO₂) coating: Enhances high-temperature and wear resistance, suitable for high-performance coatings and ceramics.
Process: Metal salts (e.g., sodium silicate, aluminum sulfate) are added to TiO₂ slurry, adjusting pH to precipitate metal oxide hydrates.
Composite oxide coating
Principle: Coating with two or more metal oxides (e.g., Al₂O₃-SiO₂, ZrO₂-SiO₂) combines the advantages of each component.
Characteristics: Offers superior overall performance. For example, Al₂O₃-SiO₂ coating improves both dispersion and weather resistance, suitable for high-performance automotive paints and coil coatings.
Salt coating
Principle: Metal salts (e.g., phosphates, silicates, sulfates) form insoluble salt layers on the TiO₂ surface.
Common Types:
- Aluminum phosphate coating: Enhances weather resistance and anti-powdering ability, commonly used in outdoor coatings.
- Zinc sulfate coating: Improves surface charge properties, reduces agglomeration, and enhances dispersion.
Organic coating modification
Through the reaction of organic compounds with the hydroxyl groups on the surface of titanium dioxide, an organic molecular layer is formed to improve its compatibility with organic media.
Coupling agent coating
Principle: Coupling agent molecules (e.g., silanes, titanates, aluminates) have an amphiphilic structure, with one end bonding to TiO₂ hydroxyl groups and the other reacting with organic matrices (e.g., resins, polymers).
Function:
- Silane coupling agents: Improve TiO₂ dispersion in aqueous systems, commonly used in water-based coatings and inks.
- Titanate / Aluminate coupling agents: Enhance compatibility in oily systems like plastics and rubbers, reducing agglomeration during processing.
Surfactant coating
Principle: Surfactants (e.g., fatty acids, sulfonates, quaternary ammonium salts) attach to the TiO₂ surface through physical adsorption or chemical reactions, forming a charge or hydrophobic layer.
Function:
- Anionic surfactants (e.g., stearic acid): Improve dispersion in oily media, commonly used in plastics and rubber.
- Cationic surfactants (e.g., dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride): Suitable for polar systems, enhancing stability.
Polymer coating
Principle: Polymer grafting (e.g., acrylates, epoxy resins, siloxanes) is achieved through polymerization reactions on the TiO₂ surface.
Function: Forms a thick coating layer, further isolating chemical corrosion, improving weather resistance and mechanical properties. Enhances compatibility with specific resins, suitable for high-performance composites and coatings.
Silicone coating
Principle: Polyorganosiloxanes (e.g., silicones, silicone resins) coat TiO₂ particles due to their low surface energy properties.
Function: Reduces surface tension, enhances dispersion and smoothness, commonly used in inks and cosmetics.
Composite coating modification
Combining the advantages of inorganic and organic coatings, double coating is carried out in stages or simultaneously to achieve complementary performance.
Inorganic first then organic coating
Process: First, form a physical barrier with inorganic oxides (e.g., SiO₂), then modify with coupling agents or polymers for organic enhancement.
Characteristics: Balances weather resistance and compatibility, such as in high-weather-resistance architectural coatings or OEM automotive paints.
Inorganic-organic synchronous coating
Process: Simultaneously introduce inorganic and organic coatings in the same reaction system to form a core-shell structure.
Characteristics: The coating layers bond more tightly, leading to significant performance improvements. Suitable for high-end applications, such as aerospace coatings and nanocomposites.
Other special coating technologies
Nano coating
Principle: Use nanomaterials (e.g., nano SiO₂, nano ZnO) for coating to enhance UV shielding ability and transparency, commonly used in sunscreen cosmetics and optical coatings.
Microcapsule coating
Principle: Encase TiO₂ particles in polymer microcapsules, releasing TiO₂ by controlling the capsule rupture conditions (e.g., temperature, pH). Suitable for smart coatings and controlled-release systems.
Conclusion
The choice of titanium dioxide coating modification should be based on the application scenario (e.g., coatings, plastics, inks, cosmetics) and performance requirements (e.g., weather resistance, dispersion, compatibility).

For example:
- Outdoor coatings: Inorganic oxides (e.g., Al₂O₃-SiO₂) or composite coatings are preferred to enhance weather resistance.
- Plastic processing: Coupling agents or surfactants are used to improve dispersion and processing performance.
- High-end applications: Composite or nano coatings enable multifunctional synergistic optimization.

Epic powder
Epic Powder, 20+ years of work experience in the ultrafine powder industry. Actively promote the future development of ultra-fine powder, focusing on crushing,grinding,classifying and modification process of ultra-fine powder. Contact us for a free consultation and customized solutions! Our expert team is dedicated to providing high-quality products and services to maximize the value of your powder processing. Epic Powder—Your Trusted Powder Processing Expert !
