The main types of lithium battery negative electrode materials include graphite-based materials (such as artificial graphite and natural graphite) and non-graphite-based materials (such as silicon-based anode materials). Below is the common production process for these materials:
Production Process of Artificial Graphite Negative Electrode Material
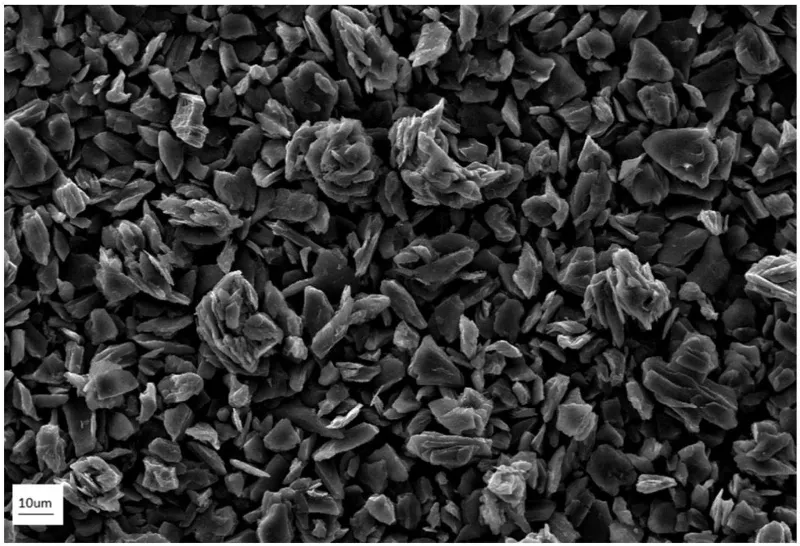
Pre-treatment
Graphite raw materials and asphalt are mixed according to product requirements, such as 100: (5-20). The mixture is transferred to a hopper via a vacuum feeder. From there, it enters an air jet mill for air flow grinding. The raw and auxiliary materials, initially 5-10mm in size, are ground to 5-10 microns. After grinding, a cyclone dust collector is used to gather the desired particle sizes, with a dust collection rate of about 80%. The tail gas is filtered by the filter element and discharged. The dust removal efficiency is greater than 99%.

Granulation
This process is divided into pyrolysis and ball mill screening steps.
Pyrolysis Process:
The intermediate material is placed in a reactor. Nitrogen replaces the air inside the reactor. The reactor is sealed and electrically heated according to the temperature curve, under a pressure of 2.5kg. It is stirred at 200-300°C for 1-3 hours, then heated further to 400-500°C. The material is stirred to form particles sized 10-20mm. It is then cooled and discharged, resulting in intermediate material 2.
Ball Mill and Screening Process:
The intermediate material 2 is fed into the ball mill via vacuum feeding. The 10-20mm material is ground to 6-10 microns. The powder is then transferred to a screening machine via a pipeline. The screened material is measured and packaged by an automatic packing and metering device, producing intermediate material 3. The oversized material is returned to the ball mill for further grinding via vacuum conveyance.

Graphitization
The product is placed in a protective medium inside the graphitization furnace and heated to high temperatures. This process transforms the disordered hexagonal carbon atom planes in two-dimensional space into an ordered three-dimensional arrangement, giving it a graphite structure. There are two main graphitization methods: intermittent and continuous. The most commonly used are the Acheson and box-type graphitization furnaces.
In the Acheson process, the anode material is evenly placed in graphite crucibles. These crucibles are lifted by an overhead crane and placed flat in the furnace. Resistor material is placed around the graphite crucible at the furnace core. The crucible is covered with insulation material to fill the furnace. The furnace is heated by electrodes on both sides. Once the furnace reaches the required temperature, the top is covered, and a gas collection hood is installed. The furnace temperature rises to 2800-3000°C. The carbon material inside the crucible undergoes high-temperature treatment, which reduces impurities from the amorphous carbon microcrystalline structure, resulting in a graphite crystal structure.
Ball Milling and Screening
The graphitized material is vacuum-fed into a ball mill for physical mixing and grinding. A 270-mesh molecular sieve is used for screening. The screened material is then inspected, weighed, packaged, and stored. Any oversized material is further ball milled to meet particle size requirements before being screened again.
Production Process of Natural Graphite Negative Electrode Materials
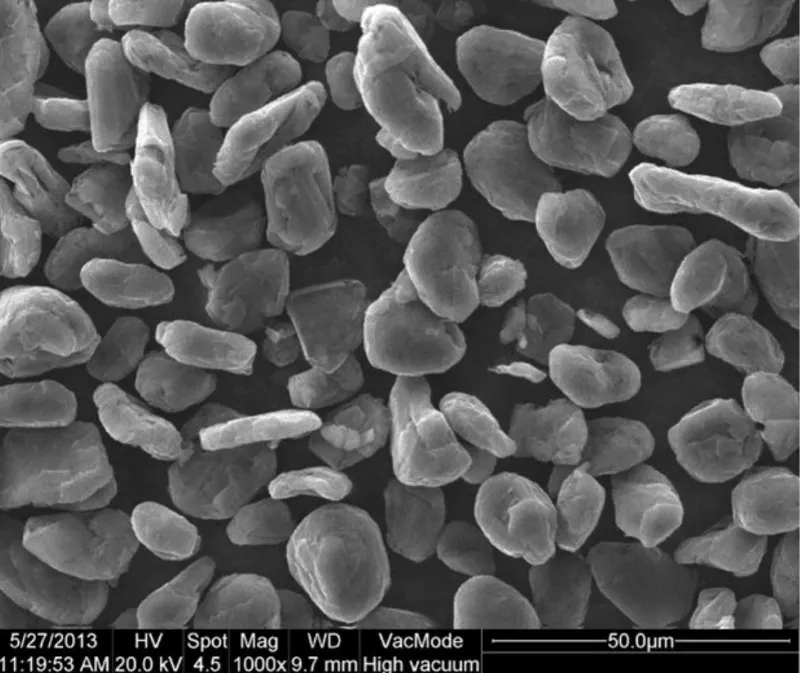

- Graphite Ore Mining and Flotation Classification:
Graphite ore is mined from natural graphite deposits. The ore is then processed through flotation and other methods to remove impurities. This results in graphite particles with specific particle size and purity. - Spheronization:
Natural graphite particles are processed using air impact or grinding methods for spheronization. This makes the graphite particles more uniform in shape, improving their bulk density and rate performance. - Purification and Drying:
The spheronized graphite particles undergo chemical purification to remove impurities and harmful elements. Afterward, the particles are dried to remove moisture. - Surface Modification:
Chemical or physical methods are used to modify the surface of the graphite particles. This may include coating with conductive materials or surface treatment to improve their electrochemical performance. - Mixing and Screening:
The surface-modified graphite particles are mixed with other additives, such as conductive agents and binders. The mixture is then screened to remove impurities and substandard particles. - Magnetic Removal and Packaging:
The screened graphite particles undergo magnetic removal to eliminate any magnetic materials. Afterward, the materials are packaged to produce the final natural graphite negative electrode product.
Production Process of Silicon-Based Negative Electrode Materials
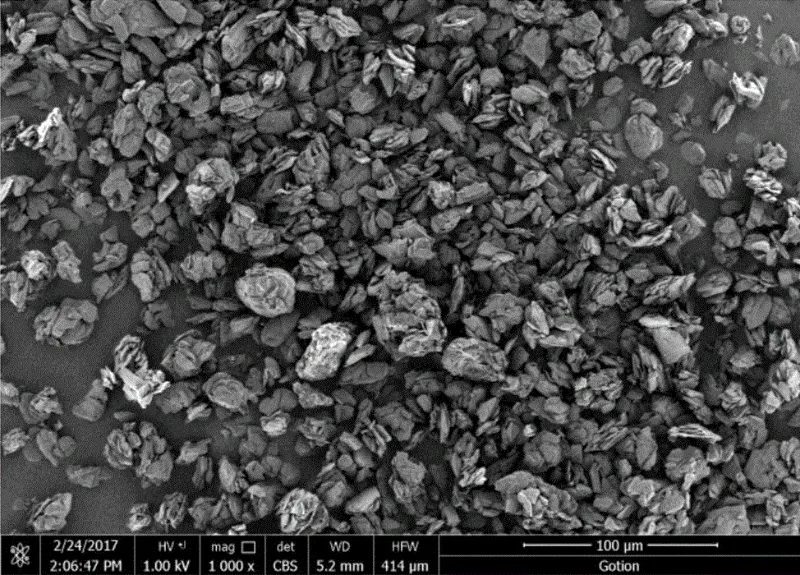
Using Carbon-Coated Silicon Dioxide as an Example:
- Silicon Source Preparation:
Silicon nanoparticles or thin films are prepared using methods like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or physical vapor deposition (PVD). - Silicon Dioxide Synthesis:
The silicon source material reacts with an oxidizing agent under specific conditions to form silicon dioxide (SiO). - Carbon Coating:
A carbon layer is coated on the surface of silicon dioxide using methods such as chemical vapor deposition, physical vapor deposition, or the sol-gel method. This forms the carbon-coated silicon dioxide composite material. - Post-treatment:
The carbon-coated silicon dioxide composite material undergoes post-treatment processes, such as crushing, grading, and drying. The result is a silicon-based negative electrode material with uniform particle size and stable performance.
Epic Powder
Epic Powder, 20+ years of work experience in the ultrafine powder industry. Actively promote the future development of ultra-fine powder, focusing on crushing, grinding, classifying and modification process of ultra-fine powder. Contact us for a free consultation and customized solutions! Our expert team is dedicated to providing high-quality products and services to maximize the value of your powder processing. Epic Powder—Your Trusted Powder Processing Expert !
